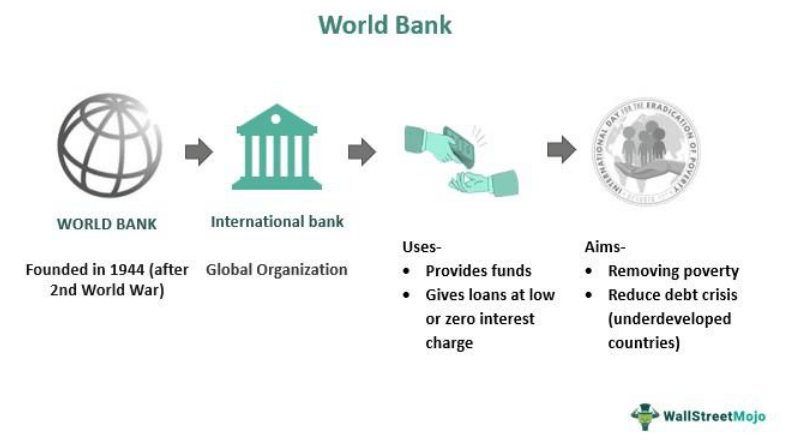
The World Bank is an international financial institution that was established in 1944 with the goal of reducing poverty and promoting economic development. Over the years, it has played a pivotal role in empowering sustainable development and driving positive change across the globe. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the World Bank’s history, its commitment to sustainable development, impactful projects, global prosperity, sustainable development goals, success stories, driving economic growth and inclusion, and its collaborative approach to development. History of World Bank
| Established | July 7, 1944 (78 years ago) |
| Type | International financial institution |
| Headquarters | 1818 H Street, NW Washington, D.C., U.S |
| Membership | 189 countries (IBRD) 174 countries (IDA) |
| Key people | Ajay Banga (President) Axel van Trotsenburg (MD) Anshula Kant (MD and CFO) Indermit Gill (Chief Economist) |
| Parent organization | World Bank Group |
| Website | www.worldbank.org |
History of the World Bank:
The history of the World Bank can be traced back to the aftermath of World War II. In July 1944, representatives from 44 countries gathered in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, United States, to discuss the establishment of a financial institution that would facilitate the reconstruction efforts and promote economic stability. The delegates at the Bretton Woods Conference agreed to create the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), which later became known as the World Bank. The IBRD’s primary objective was to provide financial and technical assistance to countries for the reconstruction of war-torn Europe and the development of other regions.

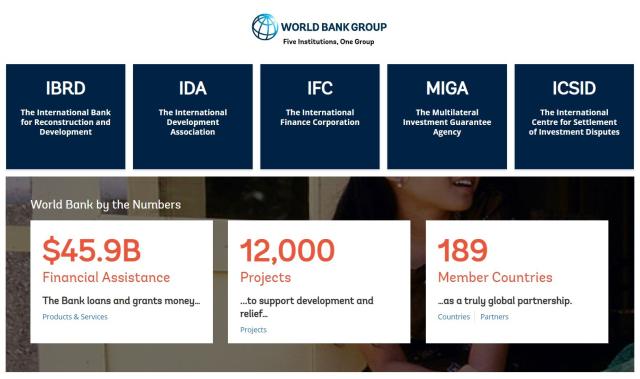
World Bank Group
The World Bank Group is an international financial institution that consists of five institutions working together to achieve their shared goals of reducing poverty and promoting shared prosperity.
1. International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD):
The IBRD provides loans and other financial assistance to middle-income and creditworthy low-income countries to support projects and programs that promote economic development, reduce poverty, and improve living standards. It focuses on financing infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and power plants, as well as investments in human capital, such as education and healthcare.
2. International Development Association (IDA):
The IDA provides grants and low-interest loans to the world’s poorest countries, primarily in Sub-Saharan Africa and some other regions. It aims to support these countries in overcoming the challenges of extreme poverty by funding projects that address issues such as healthcare, education, agriculture, and infrastructure development.
3. International Finance Corporation (IFC):
The IFC is the private sector arm of the World Bank Group. It focuses on promoting private sector investment in developing countries to stimulate economic growth, create jobs, and improve living standards. The IFC provides financing, advisory services, and technical assistance to private companies, supporting projects in sectors such as manufacturing, infrastructure, and financial services.
4. Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA):
MIGA provides political risk insurance and credit enhancement to investors and lenders involved in projects in developing countries. Its purpose is to promote foreign direct investment by protecting investors against non-commercial risks, such as political instability, expropriation, and breach of contract. By providing guarantees, MIGA helps attract investment to countries that may otherwise be considered risky.
5. International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID):
The ICSID is an arbitration institution that provides a forum for resolving investment disputes between governments and foreign investors. It offers a neutral and impartial venue for parties to resolve conflicts related to international investment, ensuring a fair and transparent process.
Empowering Sustainable Development:
It recognizes the interconnectedness between economic growth, social progress, and environmental sustainability. The Bank promotes sustainable development by supporting projects and programs that balance economic, social, and environmental considerations. Its initiatives aim to create lasting positive impacts by fostering inclusive growth, promoting social equity, and preserving natural resources.

World Bank’s Impactful Projects:
The World Bank has been involved in numerous impactful projects that have made a tangible difference in the lives of people around the world. These projects span a wide range of sectors, including infrastructure development, agriculture, education, healthcare, and environmental conservation. By investing in critical infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and power plants, the Bank stimulates economic activity and enhances access to essential services. It also supports social development projects like education and healthcare initiatives, improving human capital and promoting social well-being.
World Bank’s Commitment to Global Prosperity:
The World Bank is deeply committed to global prosperity and shared growth. It strives to reduce poverty and inequality, create jobs, and foster inclusive economic development. By providing financial resources, technical expertise, and policy advice, the Bank works closely with governments and stakeholders to develop effective strategies and policies that drive sustainable and equitable growth. It supports countries in formulating and implementing development plans that align with their specific needs and goals.
World Bank’s Sustainable Development Goals:
The World Bank aligns its efforts with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The SDGs provide a comprehensive framework for addressing global challenges, including poverty, hunger, climate change, and inequality.
World Bank’s Success Stories:
The World Bank has a rich portfolio of success stories that highlight the transformative power of its projects and initiatives. These success stories showcase the positive impact on individuals, communities, and nations. They range from empowering communities through access to clean water and sanitation to supporting entrepreneurship and job creation. By investing in sustainable development, the Bank has helped improve the lives and livelihoods of millions of people worldwide.

Driving Economic Growth and Inclusion:
The World Bank recognizes that driving economic growth and inclusion is essential for sustainable development. It promotes financial innovations and provides financial assistance to countries to stimulate economic activity, create employment opportunities, and foster entrepreneurship. The Bank supports countries in strengthening their financial systems, improving access to finance, and promoting financial inclusion.
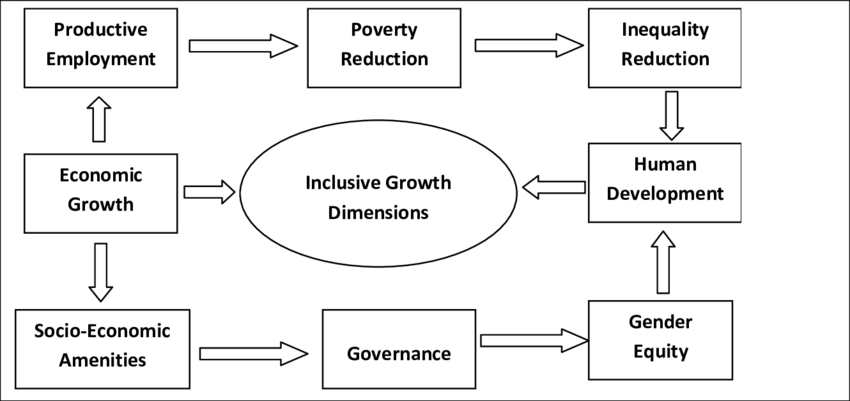
World Bank’s Collaborative Approach to Development:
Collaboration is a core principle of the World Bank’s approach to development. The Bank believes that partnerships with governments, civil society organizations, the private sector, and other stakeholders are crucial to achieving meaningful and sustainable impact. By leveraging the expertise, resources, and knowledge of various stakeholders.
In conclusion
The World Bank’s history is rooted in its mission to reduce poverty and promote economic development. Its commitment to empowering sustainable development is reflected in its impactful projects, focus on global prosperity and alignment with the Sustainable Development Goals. TodayAims.com History of World Bank

